by The Implant Guy | Nov 19, 2024 | Blog
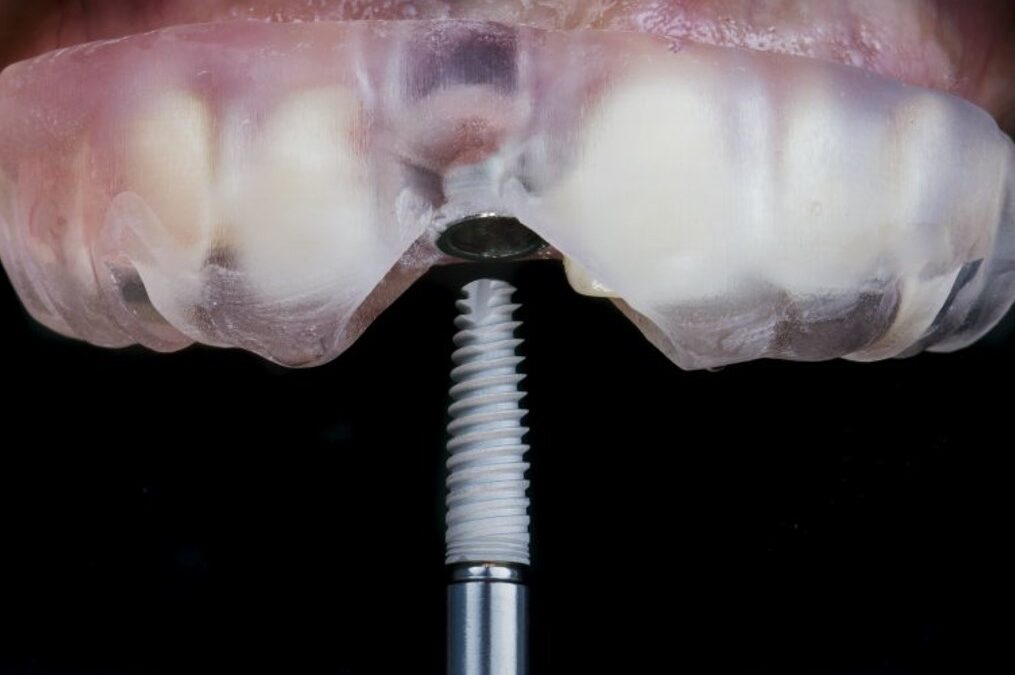
Guided implant surgery
A brief history for guided implant surgery
The Principle
The stages of guided implant planning
Production via 3D printing
The various types of surgical guides
Guided implant surgery software and systems
The advantages of guided surgery


